Legal cases
- Poisoning
- Drowning
- Electric
current/ electrocution
- Accidents
- Burns
- Eaten
by or attack by wild animals
Protocol for legal case
ü When
legal case is there we need to follow common protocol for the legal protocol
ü Panchanama
– request letter from police,
ü If
you don’t have some necessary materials you may send demand note to police
ü All
necessary arrangement should be make available by the police in legal matter
ü Collection
of material protocol
ü If
carcass is completely autolized – need to carry the postmortem examination and
collect what ever available in that dead body.
ü Collect
material as per the norms
o In
salt
o In
glycerin phosphate buffer
o Alcohol/
spirit etc
ü Seal
it and hand over to police.
1. Poisoning
ü Mostly
sudden death are there
ü Congestion
of all mucous membranes, serosae, mucosae, pin point hemorrhages on vital
organs
ü Left
chamber of heart generally empty
ü Don’t
write name of any specific toxins unless you have laboratory report with you
from authorized laboratory
ü The
lesions were suggestive of hypovolemic shock caused due to toxemia; however the
final cause of death can be drawn after the report of forensic laboratory.
ü This
is to be write in any legal case, when you have sent the samples to forensic
labs.
ü E.g.
urea poisoning, insecticide / pesticide
2.
Drowning
ü You
get dead body of animal floating in water
o Well/
river/ pond etc.
ü Need
to differentiate based on lesions observed.
ü Many
people says – water, algae, sink in water etc. etc. sink test done by some
peoples
ü Just
understand the mechanism of death when water / liquid enter into trachea/
respiratory tract.
ü Basic
inflammation rule- reaction of live tissue to the irritant.
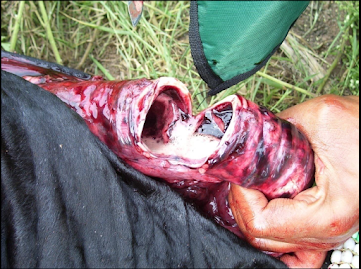
ü Lesions:
o eyes
are opened,
o Trachea
severely congested, edematous, hemorrhages in lungs, red colored froth in
trachea and bronchi, emphysema of lungs at margins, pin point hemorrhages on
endocardium, mesenteric blood vessels are engorged with blood.
o Change
in osmotic pressure in lung tissues, ruptured capillaries – blood in alvelolar
lumens + mixed with water- hemolysis of blood– extensive movements of lung
–churning of air and water- produce red colored froth
ü If
animal die before reach to water – no above lesions- clear water without
redness,no emphysema no inflammations
3.
Electric current/ electrocution
ü Entry
point -exit point
ü Many
times no direct contact of live wire
ü Circumstantial
evidences need to be noted carefully (live wire on wet soil )
ü 180
Ampere current is sufficient to cause death in cow.
ü Storms
with electrocutions should be there
ü Signs
and lesions are observed in one animal but other animals did not showed any
external lesions
ü Electric
spark – heavily charged electrons at centre, but areas around the spark is charged
with electros and all the death phenomenon is observed due to these electrons.
ü Around
20 to 25 feet area around the spark is charged with electrons.
ü Spark
may fall on one animal but animals around that spark are also found dead.
ü Once
electron enter into body all the conducting mechanisms is get increase thousand
fold times- heart conduction, nerve impulses, voluntary and involuntary nerve tissues
ü Disparity
between heart and lung synchronization
ü Hypovolemic
shock and death.
ü Eyes
are open
ü External
marks may be / may not be present.
ü Hemorrhages
and blood clots in bronchus.
ü Severe
emphysema of lungs, hemorrhages
ü Change
in shape of heart scanty of blood clots in heart chambers.
ü Mesenteric
blood vessels are engorged
ü This
is true in all species including human being.
4.
Accidents
ü Road
accident- dead before accident of died due
to accident. (wild animals)
ü Some
tribal communities kill the animals by poisoning and throw them on high way
ü Again
same logic of inflammation
ü Fractured
portion will have inflammation around the surrounding tissues- musculature/ blood
clots and inflammatory line
ü The
lesions were suggestive of hypovolemic shock due to mechanical injury.
ü No
need to write truck/ car/ bike etc.
ü As
can’t be diagnosed on post mortem lesions.
5.
Burns
ü If
carcass is burn completely and only char/ char coal is there
ü One
line report – carcass is completely charred due to burn.
ü But
problems with incompletely burned carcass,
many time to destroy the evidence peoples
are doing such things
ü They
may poison the animal and try to burn it
and want to show that died in burn.
ü Again
same basic logic of inflammation is to be applied- zone of inflammation, exudation
etc.
ü Eyes
are bulged out, mouth cavity swollen and many carbon particles in the cavity, trachea
will be edematous, inflamed and carbon particles in to the deeper portion of
trachea and bronchi.
ü If
all these lesions are there – then burn
ü Absent
– no burn.
6.
Eaten by or attack by wild animals
ü Many
times to get compensation from govt. farmers throw their dead animals in jungle
areas and will complaint to you that his animal
has been attacked by wild animals.
ü As
you reach to carcass you will get only part of skeleton.
ü Ideally
you need to say that -the organs are missing hence cause of death cannot be drawn.
(Political issues)
ü If
whole body is there with injuries at neck/ jugular veins/ back
ü You
may say that animal by died due to hypovolemic shock caused due to hemorrhages,
and these hemorrhages might be occurred due to unknown canines / wild animals. (Need
all circumstantial evidences from forest department- foot print matching etc.)
Special Thanks to:
Dr. D.S. Suryawanshi
Director
Omega Laboratories




Post a Comment