Peste des petits ruminants
- PPR is a highly contagious viral disease of sheep
and goats which is characterized by fever, stomatitis, diarrhea,
oculo-nasal dischargesand pneumonia with foul offensive breath.
- OIE-Listed
disease
Synonym :
- Pseudo-rinderpest
- Goat Plague
- Pest of Small Ruminants
- Pest of Sheep and Goats
- Kata
- Stomatitis-Pneumoenteritis Syndrome
- Pneumoenteritis Complex
Etiology:
•
Peste des petits ruminants virus – SS RNA
•
Genus: Morbillivirus
•
Family: Paramyxoviridae
•
Other
members of the family include RP, Measles virus, Canine distemper
•
Vaccination for RP can prevent PPR in ruminants
•
Serological
cross-reactivity with RP in diagnostics
Host:
•
Primarily
a disease of goats and sheep
•
Cattle
and pigs seroconvert but do not develop or transmit disease
•
Wild
ungulates can be affected
Transmission:
•
Direct
contact
• Nasal/ocular secretions
• Urine, saliva, and blood
•
Contaminated
food or water
•
Indirect
contact
• Fomites
Risk
factor:
·
Kids
> 4 month and < 1 year are more susceptible for PPR
·
Resistance
in Sahelian breed.
Pathogenesis:
Virus reach to nasopharyngeal mucosa
⇓
And binds to host (CD150) on activated T cells, B cells and dendritic cells of tonsils and regional lymphnodes
⇓
Virus
replication
⇓
Go
in the blood
⇓
Viremia
⇓
dissemination to respiratory and alimentary mucosal cells
⇓
Virus replication causing focal necrosis, erosion, and fibrinous exudation (Pneumo-enteritis)
⇓
Infect
lymph nodes and GALT
⇓
destructions of lymphocytes
⇓
Immunodeficiency
⇓
Secondary
bacterial infection
⇓
Death
from severe Pneumo-enteritis
Clinical
Signs:
•
Incubation
period: 2- 10 Days
•
Peracute
•
Acute
• High fever :- 41°C/
106°F
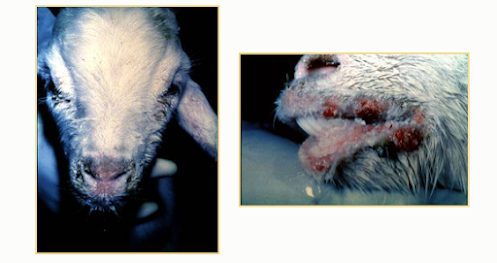
• Serous nasal, ocular
discharge becomes mucopurulent
• Hyperemic gums, necrotic oral lesions
• Profuse diarrhea, Dehydration
• Emaciation
• Erosive stomatitis,
• Conjunctivitis,
• Gastroenteritis,
• Rapid respiration, dyspnea
• Abortion
• Skin nodules around muzzle
•
Subacute
- asymptomatic disease
•
High
morbidity (up to 100%) and up to 90% mortality and death within 4-6 days.
Macroscopic Pathology:
•
Dehydrated, soiled, fetid
carcass
•
Serous or mucopurulent
oculonasal discharges
•
Inflammatory and necrotic
lesions on oral cavity and GI tract
•
Bronchopneumonia with
consolidation and atelectasis – Cranio-ventral lobes
•
Congestion and Inflammation of
upper RT
•
blood-tinged, frothy exudates
in tracheas
•
Congested, edematous and
enlarged spleen and lymph nodes
•
Hemorrhage and congestion of
cecum, colon, rectum (zebra stripes like lesions during post mortem)
•
Swelling, Congestion and
erosion of vulval or vaginal mucosa seen sometimes in PPR
Microscopic Pathology:
•
Mild multifocal tracheitis, bronchitis and necrotizing bronchiolitis, and diffuse
proliferative interstitial pneumonia
•
Focal mucosal necrosis just above basal layer which is
extending to the surface
•
Necrosis of intestinal crypts with resultant erosions
, ulcers and inflammtion
•
Syncytia; intracytoplasmic and intranuclear
eosinophilic inclusion bodies in infected epithelial cells in this case of PPR
Diagnosis
•
Clinical signs
•
Laboratory tests
•
Virus isolation
•
Agar gel immunodiffusion (AGID)
•
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
•
Complement fixation test
•
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
(RT-PCR) tests
•
Serological tests
•
Virus neutralization tests
Differential diagnosis:
• Rinderpest
•
Contagious ecthyma
•
Bacterial pneumonias
•
Heartwater
•
Pneumonic pasteurellosis
•
Contagious caprine pleuropneumonia in goats
•
Contagious bovine pleuropneumonia
•
Helminthosis
•
Coccidiosis
• Possibly
Nairobi sheep disease
Treatment
•
Hyperimmune serum
•
Symptomatic treatment
of clinical sign
• Broad-spectrum antibiotics like enrofloxcin @ 2.5-5 mg/kg
• Provided analgin or meloxicam
• Also prescribe the pest for the ulcerative stomatitis
• Intestinal astringents like creta and kaolin were administered.
• I/v fluids like dextrose normal saline(DNS) @ 10ml/ kg body weight
Control
•
PPRV vaccine
•
Focused vaccinations in high-risk populations of sheep
and goats in the herd
•
Mass vaccination into sheep and goat so achieve 70% to
89% herd immunity
•
Disinfectant use like Phenols, Sodium hydroxide
•
Two
vaccines are for PPR
ü PPR vaccine
ü Raksha PPR At 3 month of age by subcutaneous route.



Post a Comment