Principle:-
Vaginal epithelium ⇒ Bistratified cuboidal epithelium
⇓
Estrogen ⇒
Stratified squamous epithelium (> 30 cell
layers)
⇓
Maturation
Keratinized and falls in vaginal lumen
(Exfoliate)
Know the Stages of Canine Estrous Cycle
1.
Proestrus (Early & Late)
2.
Estrus
3.
Diestrus
4. Anestrus
★ There is considerable variation in the time of ovulation in relation to the onset of proestrus.
Not understood by dog breeders
⇓
They follow standard mating regimes
⇓
Thus they not covered all presented cases.
Important of Vaginal Cytology ?
⇒ To know the stages of estrous for optimum
breeding time.
⇒ Knowledge of the onset of vaginal discharge
and their type
⇒ Degree of vulvar swelling
⇒ Attitude of female towards male dog
⇒ To detect inflammation and neoplasia of the genital tract
Materials Required for
1. Glass
slide
2. Sterile
cotton swab
3. Stain
(Leishman’s or Geimsa )
4. Microscope
Technique of Vaginal Cytology:-
Carefully open the Vulva
⇓
Direct swab cranio-dorsally
⇓
Swab
the vaginal wall (gently rubbing or rolling)
⇓
Roll on glass slide (not smeared) & dry
⇓
Staining.
Staining of slide:
A. Leishman’s staining :
Pour Leishman’s solution on slide (1 minute)
⇓
Dilute the stain with equal volume of D. water
⇓
Leave it for 15-20 min
⇓
Wash slide with D.W.
⇓
Dry and Observe in 40x
B. Giemsa Staining :
Fix the slide in methyl Alcohol (2-3 Min.)
⇓
Pour Giemsa solution (10:1 to 20:1 dilution)
⇓
Leave it for 45-50 min
⇓
Wash slide with D.W.
⇓
Dry and Observe in 40x
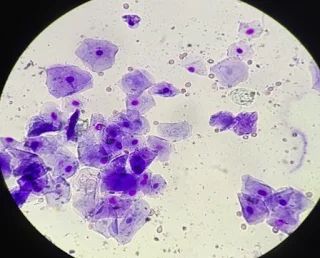
How many types of Vaginal Epithelial Cell ?
1. Basal Cells (may not be seen)
2. Parabasal Cells : ➡️ Seen O shaped oat
cereal pieces.
3. Intermediate Cells (Small & Large) ➡️ Seen fried eggs shape .
4. Superficial Cells/Cornified cells ➡️ Seen corn flakes shape
Parabasal cells :-
⇒ Small round cells with round nuclei and small
amount of cytoplasm
⇒ Uniform in size and shape.
Intermediate cells:-
⇒ May be small or large
⇒ Round nuclei, nucleus similar in size as
parabasal cells
⇒ About twice the size of parabasal cells
⇒ Cytoplasm becomes angular, irregular and
folded as cell enlarges
Superficial cells:-
⇒ Largest epithelial cell
⇒ In advancing age, the nuclei becomes small,
pyknotic and fades.
⇒ Cytoplasm may contain vacuoles with age
Superficial cells continued:-
⇒ Cornification is the degeneration process
⇒ Superficial cells are commonly called
cornified or Keraninized cells
⇒ Once nucleus is lost, become Anuclear cells
Stages of Canine Estrous Cycle
1. Proestrus (Early & Late)
2. Estrus
3. Diestrus
4. Anestrus
Proestrus:-
⇒ Swollen vulva, reddish vulvar discharge
⇒ Will not accept the male during this time
⇒ Average Duration is 9 days (with possibility
of 2-15)
⇒ Erythrocytes are numerous and gradually
decline
⇒ Neutrophils are also present
Early proestrus:-
⇒ Parabasal and intermediate cells predominate
⇒ As proestrus progresses, parabasal cells
disappear as superficial cells increase.
⇒ Erythrocytes are numerous
⇒ Neutrophils are also present
Late proestrus:-
⇒ Large intermediate and superficial cells
predominate
⇒ No parabasal cells or small intermediate
cells
⇒ Red blood cells present or absent
⇒ Less neutrophils
⇒ Bacteria often present
Estrus:-
⇒ Lasts an average of 9 days
⇒ Female accepts male
⇒ Vulvar discharge is less bloody
⇒ Vulva is softer
⇒ Sometimes bloody discharge may continue
through estrus
⇒ Superficial cells predominate (90%)
⇒ May become cornified or Keratinized
⇒ NO WBCs except at last 1-2 days of estrus
⇒ Variable RBCs
 |
Large intermediate and keratinized cells |
Estrus-Hormonal Events
⇒ Serum progesterone increases above anestrus
range
⇒ Progesterone rise begins when LH peaks
⇒ Ovulation occurs 2 days after LH peak
⇒ Eggs take an additional 2-3 days to mature
⇒ Fertile period is 4-7 days after LH peak
Diestrus:-
⇒ Abrupt decrease in superficial cells
⇒ Increase in parabasal cells and intermediate
cells
⇒ Many WBC’s, then decrease in late diestrus
⇒ Variable RBC’s
⇒ Progesterone peaks 15-30 days post estrus,
then declines
Anestrus
⇒ Transition period between two estrous cycle
⇒ 4-12 months
⇒ Parabasal and intermediate cells predominate
⇒ Few WBC’s and bacteria









Post a Comment